Interaction of Polycations with Phospholipid Membranes
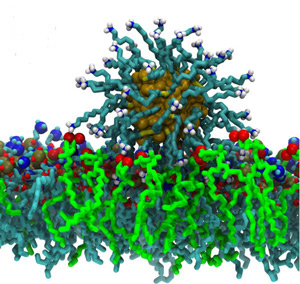
Cationic polymers are known to possess antibacterial activity: The polymers are able to either destroy bacterial membranes or largely modify their properties in such a way that the membrane damage causes cell death. We study the interactions of a wide range of cationic polymers as well as charged nanoparticles with the surface of model biological membranes in order to unlock molecular mechanisms of action of these agents on biomembranes.
Other projects:

